HyperINR: A Fast and Predictive Hypernetwork for Implicit Neural Representations via Knowledge Distillation
Qi Wu, David Bauer, Yuyang Chen, and Kwan Liu Ma
ArXiv Preprint, 2023

Abstract
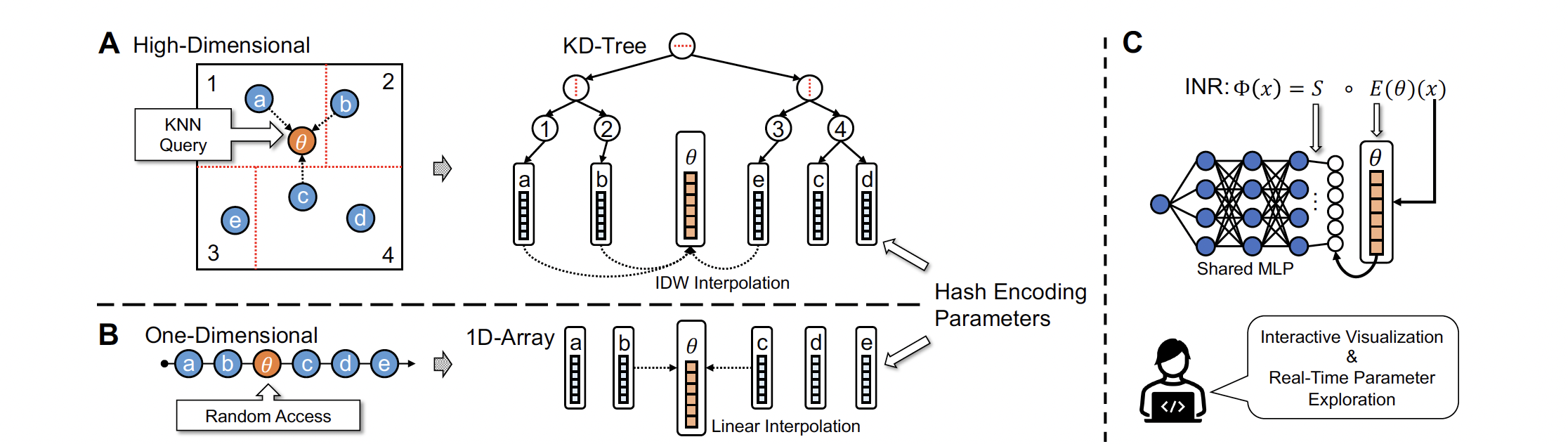
Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) have recently exhibited immense potential in the field of scientific visualization for both data generation and visualization tasks. However, these representations often consist of large multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs), necessitating millions of operations for a single forward pass, consequently hindering interactive visual exploration. While reducing the size of the MLPs and employing efficient parametric encoding schemes can alleviate this issue, it compromises generalizability for unseen parameters, rendering it unsuitable for tasks such as temporal super-resolution. In this paper, we introduce HyperINR, a novel hypernetwork architecture capable of directly predicting the weights for a compact INR. By harnessing an ensemble of multiresolution hash encoding units in unison, the resulting INR attains state-of-the-art inference performance (up to 100x higher inference bandwidth) and can support interactive photo-realistic volume visualization. Additionally, by incorporating knowledge distillation, exceptional data and visualization generation quality is achieved, making our method valuable for real-time parameter exploration. We validate the effectiveness of the HyperINR architecture through a comprehensive ablation study. We showcase the versatility of HyperINR across three distinct scientific domains: novel view synthesis, temporal super-resolution of volume data, and volume rendering with dynamic global shadows. By simultaneously achieving efficiency and generalizability, HyperINR paves the way for applying INR in a wider array of scientific visualization applications.